Description
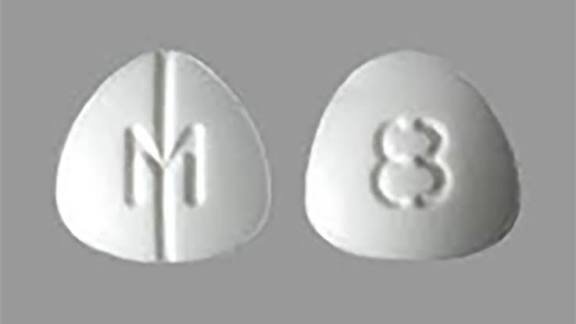
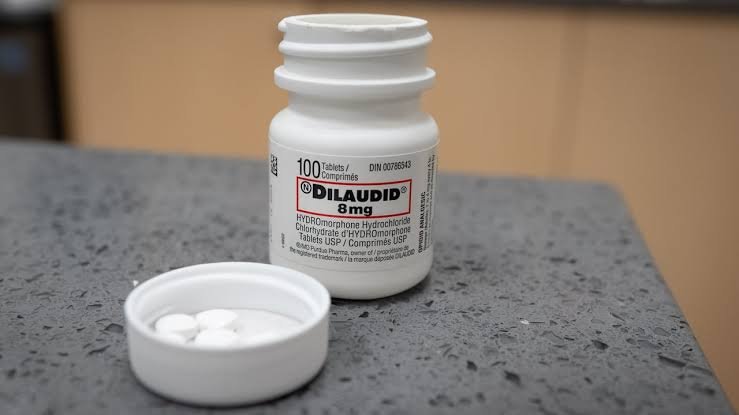
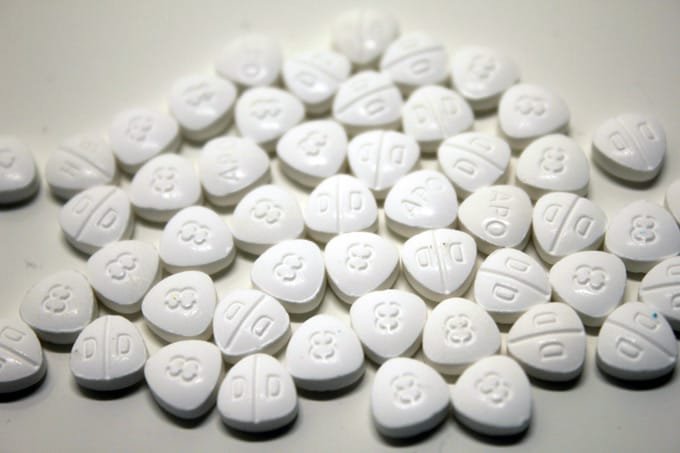
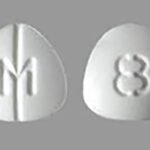
Dilaudid 8mg (hydromorphone) is a potent prescription opioid medication used for severe pain management . It works in the brain to treat moderate-to-severe pain, with effects typically felt within 1 hour. It is a white, triangular pill labeled with “P d 8”. It is classified as a Schedule 2 narcotic with a high risk of addiction and abuse.
Key Information:
- Common Use: For management of pain where other treatments are inadequate.
- Administration Frequency: It is typically administered at specific intervals as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Side Effects: Potential for severe side effects including respiratory depression, dizziness, constipation, dry mouth, nausea, and sedation.
- Risks: High potential for addiction, abuse, and physical dependence.
- Precautions: Do not use if you have severe asthma, breathing problems, or bowel blockage. Avoid alcohol and, when using, do not drive until you know how it affects you.
- Withdrawal: Abrupt discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
This medication is used to help relieve moderate to severe pain. Hydromorphone belongs to a class of drugs known as opioid analgesics. It works in the brain to change how your body feels and responds to pain.
Pill Identification
The authentic brand-name 8 mg tablet has distinct characteristics:
- Color: White.
- Shape: Three-sided (triangular).
- Imprints: One side is typically embossed with the number “8”, while the other side often features a “D” or “P d” logo.
Usage and Dosing
- Administration: It is an immediate-release tablet taken orally, typically every 4 to 6 hours as needed for pain.
- Onset and Duration: Effects usually begin within 30 to 60 minutes and last for approximately 4 to 5 hours.
- Potency: Hydromorphone is significantly stronger than morphine; 1.5 to 2 mg of Dilaudid is roughly equivalent to 10 mg of morphine.
Critical Safety Warnings
- Addiction and Abuse: Dilaudid is a Schedule II (CII) controlled substance with a high potential for abuse, addiction, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death.
- Respiratory Depression: It can cause life-threatening breathing problems, especially when first starting the medication or after a dose increase.
- Drug Interactions: Combining Dilaudid with alcohol, benzodiazepines, or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants significantly increases the risk of fatal respiratory depression.
- Common Side Effects: These include constipation, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, and dry mouth.